Dental erosion
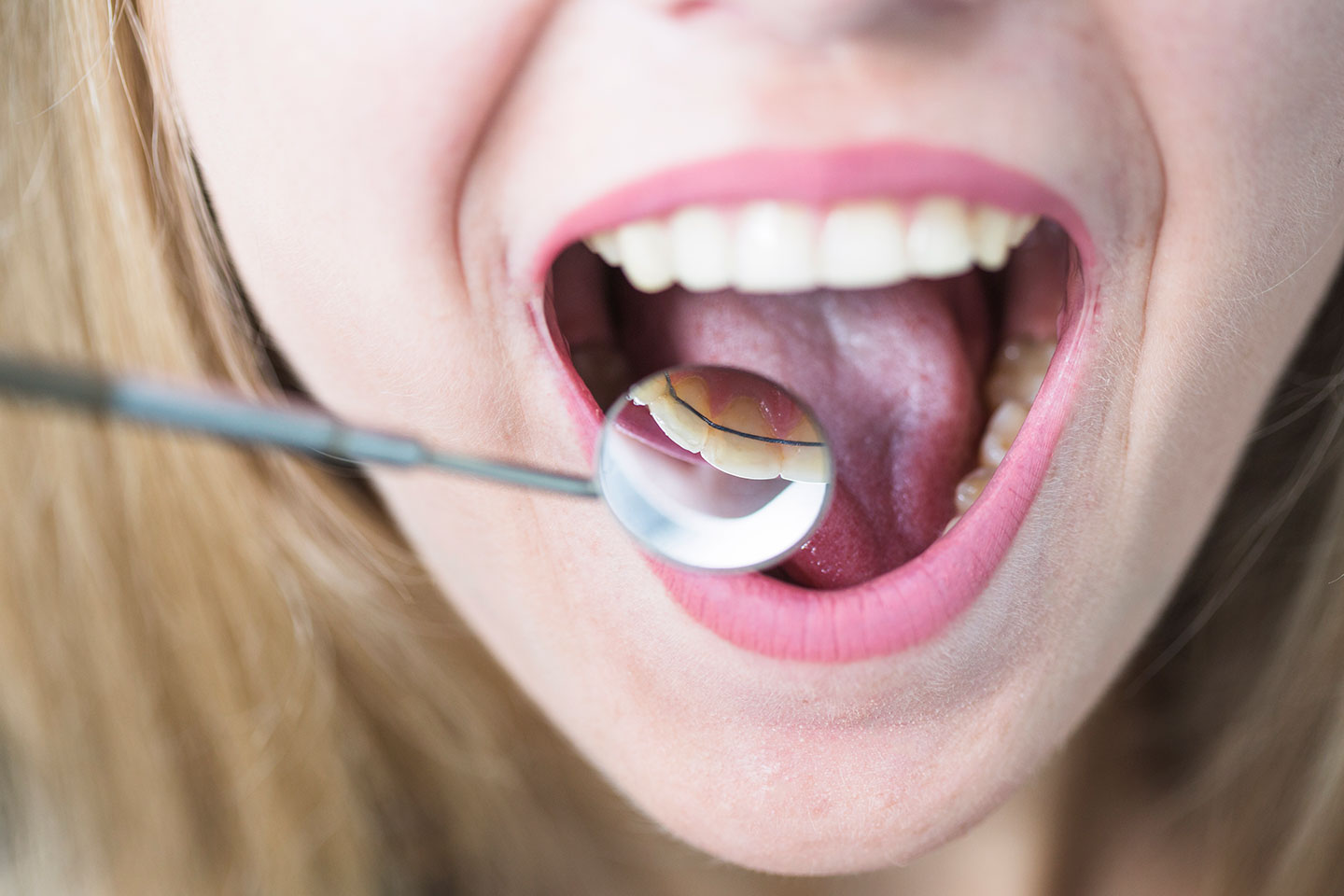
Dental erosion is permanent damage to the dental tissue on one or several teeth in a row. They are classified as non-caries tooth damage. Initially, part of the enamel is lost, then part of the dentin, and further progression may affect the tooth nerve as well. The damage results in the sensitivity of teeth to various types of stimuli (cold, sweet…). Tooth damage is located next to gums, not only causing sensitivity, but an aesthetic issue for some patients.
The factors that contribute to erosion development are:
- Aggressive brushing of teeth, with a hard brush, using an inadequate technique
- High acidity in the mouth
It can occur as a consequence of consuming acidic food and drinks (lemon, oranges, refreshing drinks containing sugar…) or as a consequence of gastric reflux or frequent vomiting (due to pregnancy or bulimia). A frequent mistake made by patients is teeth brushing immediately after consuming these types of food. The mouth should be rinsed with water immediately after a meal and the teeth should be brushed no sooner than 20 minutes after a meal.
Jaw parafunctions (involuntary jaw movements)
This mostly refers to teeth grinding, which results in enamel cracking
Biological factors
This refers to the saliva composition, teeth structure, soft tissue position, etc.
Certain medications
Erosion treatment is mostly performed during a single visit to a dental clinic. Erosion is managed with composite fillings with the recommendation to correct certain habits if they caused the erosion.
Fissure sealing
One of the preventive measures implemented in the period after permanent teeth growth.
Caries most frequently occur on the biting surfaces of teeth (pits and fissures), so those surfaces need to be protected.
Fissure sealing includes coating the biting surface of the teeth (most frequently the first permanent molars and other side teeth) with special sealants. Such sealants release fluoride and have a preventive effect on caries. A tooth with the fissures sealed is not completely caries-proof; it needs to be controlled and the sealant replaced after a certain period.
Local application of fluoride
This is another preventive measure.
It includes coating the teeth with fluoride-containing gels, varnishes or solutions. This can be performed by a dentist or by the patients themselves (mouth washing solutions with fluoride, toothpaste). The application of gels with a high concentration of fluoride is performed in an outpatient setting, once a year, in four serial applications. Teeth need to be cleaned of soft deposits and dental tartar before that. This is how the fluoride from the high-concentration products is installed in the dental enamel, thus increasing tooth resistance to the activity of caries-causing bacteria.
Removal of tartar and dental deposits
Microorganisms appear in the oral cavity several hours after birth. Tooth growth enables the development of a complex ecosystem of microorganisms and oral cavity health depends on preserving the environment in which these organisms stay without oral structure damage.
Dental plaque occurs on teeth surfaces only hours after brushing. It is a solid, sticky mass consisting of microorganisms (bacteria). It cannot be removed by swishing and rinsing, but it may be eliminated by brushing. It is a cause of many dental issues (caries, gingivitis, periodontal disease).
Tartar is calcified (mineralized) dental plaque. This occurs when the minerals from the saliva are built into the already deposited dental plaque.
Dental plaque and tartar affect the staining of the periodontium (the support structures of the teeth – “tooth flesh”) and they cause periodontal disease. Periodontal disease occurs when the gums pull away from the teeth, there is resorption of bones, resulting in the loosening and “resurfacing” of teeth, which eventually fall out.
In order to prevent this, we recommend professional teeth cleaning every six months. With the correct maintenance of oral hygiene and our additional control, you can prevent many dental diseases and diseases of the oral cavity soft tissues and maintain a beautiful smile.